Data has become a valuable resource in today’s world, and organizations are continuously striving to leverage it to make informed decisions. With the vast amount of data available, it can be challenging to make sense of it all. That’s where Power BI comes in – a business analytics solution by Microsoft that empowers organizations to visualize, analyze, and share data. Power BI reporting is an essential aspect of the Power BI platform, allowing users to create, design and share insightful reports. In this article, we’ll dive into how Power BI reporting works and explore all the aspects of creating reports using Power BI.
Overview of Power BI Reporting:
Planner Power BI reporting allows users to create and share interactive visualizations and reports based on their data. It enables users to transform their data into meaningful insights, dashboards, and reports, which can be used for data-driven decision-making. Power BI reports are created using a drag-and-drop interface, which makes it easy for users to build compelling visuals, charts, and tables.
Components of Power BI Reporting:
Data Sources:
Power BI reporting starts with data sources. These can be various data sources, such as Excel spreadsheets, SQL databases, cloud-based data storage services, or other data management tools. Power BI provides a range of connectors that allow users to access data from different sources. Users can also create custom connectors to integrate with any data source.
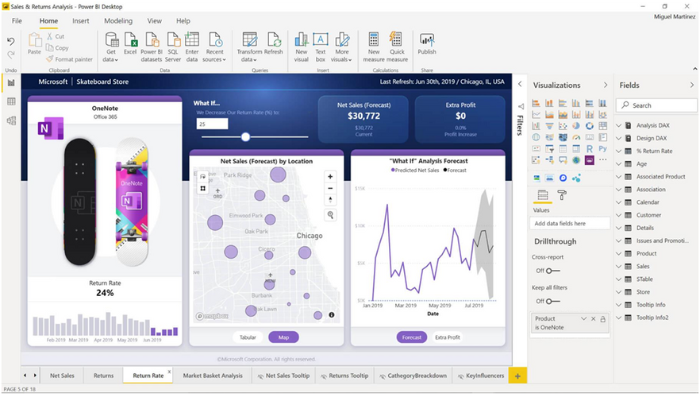
Data Modeling:
Once data sources are connected, the next step is to model the data. This involves cleaning, transforming, and shaping the data to make it suitable for reporting. Power BI provides various tools, such as Power Query and Power Pivot, to transform and model data. Users can also create relationships between different tables and define hierarchies and calculations.
Visualization:
The core of Power BI reporting is visualization, which involves creating compelling charts, graphs, and other visuals to represent data. Power BI provides various visualization types, such as bar charts, line charts, tables, maps, and gauges. Users can customize the look and feel of these visuals to suit their needs.
Data Analysis:
Power BI also provides powerful data analysis tools, such as DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) and Quick Measures, to perform advanced calculations and analysis on data. These tools enable users to gain insights from data that would be difficult to obtain using traditional reporting methods.
Sharing and Collaboration:
Finally, Power BI reporting allows users to share and collaborate on reports with others. Reports can be shared through various channels, such as email, SharePoint, and Power BI Service. Users can also collaborate on reports in real-time, enabling teams to work together to create insightful reports.
Creating Reports Using Power BI:
Connect to Data Sources:
To create a report using Power BI, the first step is to connect to data sources. Power BI provides a range of connectors that allow users to access data from different sources. Users can also create custom connectors to integrate with any data source.
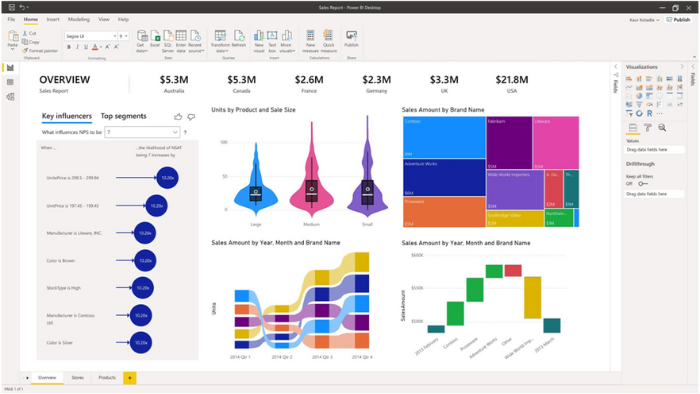
Create Data Models:
Once data sources are connected, the next step is to create data models. This involves cleaning, transforming, and shaping the data to make it suitable for reporting. Power BI provides various tools, such as Power Query and Power Pivot, to transform and model data. Users can also create relationships between different tables and define hierarchies and calculations.
Create Visualizations:
The core of Power BI reporting is visualization, which involves creating compelling charts, graphs, and other visuals to represent data. Power BI provides various visualization types, such as bar charts, line charts, tables, maps, and gauges. Users can customize the look and feel of these visuals to suit their needs.
Apply Filters and Slicers:
To make reports more interactive, users can apply filters and slicers to data visuals. Filters allow users to narrow down data by selecting specific values, while slicers allow users to slice data by different dimensions. Filters and slicers can be applied to individual visuals or to the entire report.
Add Calculated Fields:
Power BI provides advanced data analysis tools, such as DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) and Quick Measures, to perform calculations and analysis on data. Users can create calculated fields to define custom calculations and metrics that are not included in the original data source. Calculated fields can be used in visuals and other parts of the report.
Create Reports:
Once data models and visuals are created, users can start building reports by arranging and formatting visuals on report pages. Users can add text boxes, images, and other elements to provide context and explanation for the visuals. Power BI provides various formatting options, such as colors, fonts, and themes, to customize the appearance of the report.
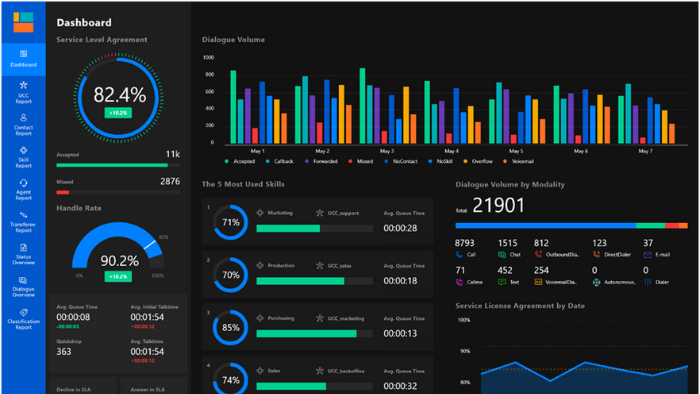
Share and Collaborate on Reports:
Power BI allows users to share and collaborate on reports with others. Reports can be shared through various channels, such as email, SharePoint, and Power BI Service. Users can also collaborate on reports in real-time, enabling teams to work together to create insightful reports. Power BI also provides various security and access control options to ensure that reports are shared securely.
Power Bi is a Revolution to the Project Management Industry
Netsuite Power Bi is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the project management industry by providing users with a suite of tools to visualize, analyze and share data. With Power BI, project managers can make informed decisions based on data-driven insights, enabling them to optimize project performance, reduce costs and improve project outcomes. In this article, we will explore how Power BI is a revolution to the project management industry and the ways in which it is transforming the way project managers work.
1. Real-time Data Analysis:
One of the most significant benefits of Power BI is its ability to provide real-time data analysis. Project managers can connect Power BI to their project management software, such as Microsoft Project or Trello, to get real-time updates on project progress. Power BI provides real-time dashboards that display critical project metrics, such as task completion rates, budget spent, and project timeline, allowing project managers to make informed decisions based on up-to-date data.
2. Comprehensive Data Visualization:
Power BI provides a comprehensive suite of data visualization tools that enable project managers to create powerful visualizations of their project data. With Power BI, project managers can create interactive dashboards that display critical project metrics, such as project timeline, budget spent, and task completion rates. These dashboards can be customized to suit the needs of different stakeholders, enabling project managers to communicate project progress effectively.
3. Advanced Data Modeling:
Power BI provides advanced data modeling capabilities that allow project managers to create complex data models to represent their project data accurately. With Power BI, project managers can create custom calculations and metrics that are not included in their project management software, providing them with a more comprehensive understanding of project performance. These custom calculations and metrics can be used to create powerful visualizations that enable project managers to identify trends, patterns, and outliers in their project data.
4. Predictive Analytics:
Power BI provides advanced predictive analytics capabilities that enable project managers to make informed decisions based on predictive insights. With Power BI, project managers can use predictive analytics to forecast project outcomes, such as project timeline, budget spent, and resource allocation. These predictive insights enable project managers to make proactive decisions to optimize project performance and reduce costs.
5. Collaboration and Sharing:
Power BI provides powerful collaboration and sharing features that enable project managers to share project data with stakeholders. With Power BI, project managers can create customized reports and dashboards that are tailored to the needs of different stakeholders, such as clients, project sponsors, and project team members. These reports and dashboards can be shared securely via email, SharePoint, or Power BI Service, enabling stakeholders to stay up-to-date on project progress.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Power BI reporting is a powerful tool for creating insightful and interactive reports based on data. The drag-and-drop interface, advanced data modeling, and visualization tools make it easy for users to transform data into meaningful insights. Power BI reporting allows users to collaborate and share reports with others, making it an essential tool for data-driven decision-making in organizations. By following the steps outlined in this article, users can start creating compelling reports using Power BI.
